Snowflake HTTP Request
This guide shows you how to set up a Snowflake procedure to call agents and tools in Agent Studio.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- Snowflake instance
- OAuth Client credentials from your Alation instance or a Server Admin role to create one.
- If calling SQL-executing agents (Query, Data Product Query, Analytics, Chart Generation), you must first configure data warehouse credentials.
Step 1. Create an OAuth client in Alation
Section titled “Step 1. Create an OAuth client in Alation”Follow the Authentication Guide to create an OAuth 2.0 Client in your Alation instance.
Make sure to note down the client_id and client_secret as you will need them to obtain an access token.
For all the steps below; replace the following values:
https://[your-instance].alationcloud.com- Your Alation instance URL<client_id>- The client ID from this step<client_secret>- The client secret from this step
Step 2. Define network connectivity and secrets
Section titled “Step 2. Define network connectivity and secrets”USE DATABASE <DATABASE_NAME>;CREATE OR REPLACE NETWORK RULE alation_rule MODE = EGRESS TYPE = HOST_PORT VALUE_LIST = ('[your-instance].alationcloud.com:443');
CREATE OR REPLACE SECRET alation_client_id TYPE = GENERIC_STRING SECRET_STRING = <client_id>;
CREATE OR REPLACE SECRET alation_client_secret TYPE = GENERIC_STRING SECRET_STRING = <client_secret>;
CREATE OR REPLACE EXTERNAL ACCESS INTEGRATION alation_eai ALLOWED_NETWORK_RULES = (alation_ai_rule) ALLOWED_AUTHENTICATION_SECRETS = ( alation_client_id, alation_client_secret ) ENABLED = TRUE;Step 3. Define procedure to get access token
Section titled “Step 3. Define procedure to get access token”We can use Snowflake’s procedures to obtain an access token.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE get_alation_access_token()RETURNS STRINGLANGUAGE PYTHONRUNTIME_VERSION = 3.10HANDLER = 'run'EXTERNAL_ACCESS_INTEGRATIONS = (alation_eai)SECRETS = ( 'client_id' = alation_client_id, 'client_secret' = alation_client_secret)PACKAGES = ('snowflake-snowpark-python','requests')AS$$import requestsimport _snowflake
def run(session):
oauth_url = "https://[your-instance].alationcloud.com/oauth/v2/token/"
client_id = _snowflake.get_generic_secret_string("client_id") client_secret = _snowflake.get_generic_secret_string("client_secret")
token_resp = requests.post( oauth_url, headers={ "accept": "application/json", "content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" }, data={ "grant_type": "client_credentials", "client_id": client_id, "client_secret": client_secret }, timeout=30 ) token_resp.raise_for_status()
access_token = token_resp.json().get("access_token") if not access_token: raise ValueError(f"No access_token in response: {token_resp.text[:1000]}")
return access_token$$;You can test it by using CALL get_alation_access_token().
Step 4. Define procedure to call Alation agent or Alation tool or Alation flow
Section titled “Step 4. Define procedure to call Alation agent or Alation tool or Alation flow”We can define this procedure as follows.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE call_catalog_context_search_agent_with_token(access_token STRING, message STRING)RETURNS STRINGLANGUAGE PYTHONRUNTIME_VERSION = 3.10HANDLER = 'run'EXTERNAL_ACCESS_INTEGRATIONS = (alation_eai)PACKAGES = ('snowflake-snowpark-python','requests')AS$$import requestsimport json
def _extract_assistant_content(obj): mm = obj.get("model_message") if isinstance(obj, dict) else None if not isinstance(mm, dict): return None parts = mm.get("parts") if not isinstance(parts, list) or not parts: return None p0 = parts[0] if not isinstance(p0, dict): return None return p0.get("content")
def run(session, access_token, message):
ai_url = ( "https://[your-instance].alationcloud.com/ai/api/v1/chats/agent/default/catalog_context_search_agent/stream" )
resp = requests.post( ai_url, headers={ "Content-Type": "application/json", "Accept": "text/event-stream", "Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}" }, json={"message": message}, stream=True, timeout=60 ) resp.raise_for_status()
last_json_obj = None first_content = None
for raw_line in resp.iter_lines(decode_unicode=True): if raw_line is None: continue line = raw_line.strip() if not line: continue if line.startswith(":") or line.lower().startswith("event:"): continue if line.lower().startswith("data:"): payload = line[5:].strip() if payload == "[DONE]": break
try: obj = json.loads(payload) except Exception: continue
last_json_obj = obj content = _extract_assistant_content(obj) if content and not first_content: first_content = content
if isinstance(last_json_obj, dict): content = _extract_assistant_content(last_json_obj) if content: return content
if first_content: return first_content
# If nothing matched, return something helpful ct = resp.headers.get("content-type") return f"No assistant content parsed. content-type={ct}"$$;We now test this by using the following.
CALL call_catalog_context_search_agent_with_token( '<PASTE_ACCESS_TOKEN_FROM_STEP_3_HERE>', 'What information can you provide about our data catalog?');Step 5: Define the procedure to call Alation tools from Snowflake agents
Section titled “Step 5: Define the procedure to call Alation tools from Snowflake agents”The procedure can be defined as follows.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE call_catalog_context_search_agent(message STRING)RETURNS STRINGLANGUAGE SQLAS$$DECLARE token STRING; answer STRING;BEGIN -- Step 1: get token (returns a 1-row resultset with one column) CALL get_alation_access_token(); SELECT $1::STRING INTO :token FROM TABLE(RESULT_SCAN(LAST_QUERY_ID()));
-- Step 2: call agent with token CALL call_catalog_context_search_agent_with_token(:token, :message); SELECT $1::STRING INTO :answer FROM TABLE(RESULT_SCAN(LAST_QUERY_ID()));
RETURN answer;END;$$;We can now test this as follows.
CALL call_catalog_context_search_agent( 'What information can you provide about our data catalog?');Step 6: We can add the above defined procedure as an external tool for the agent
Section titled “Step 6: We can add the above defined procedure as an external tool for the agent”When defining a Snowflake agent, we can add a custom tool as follows:
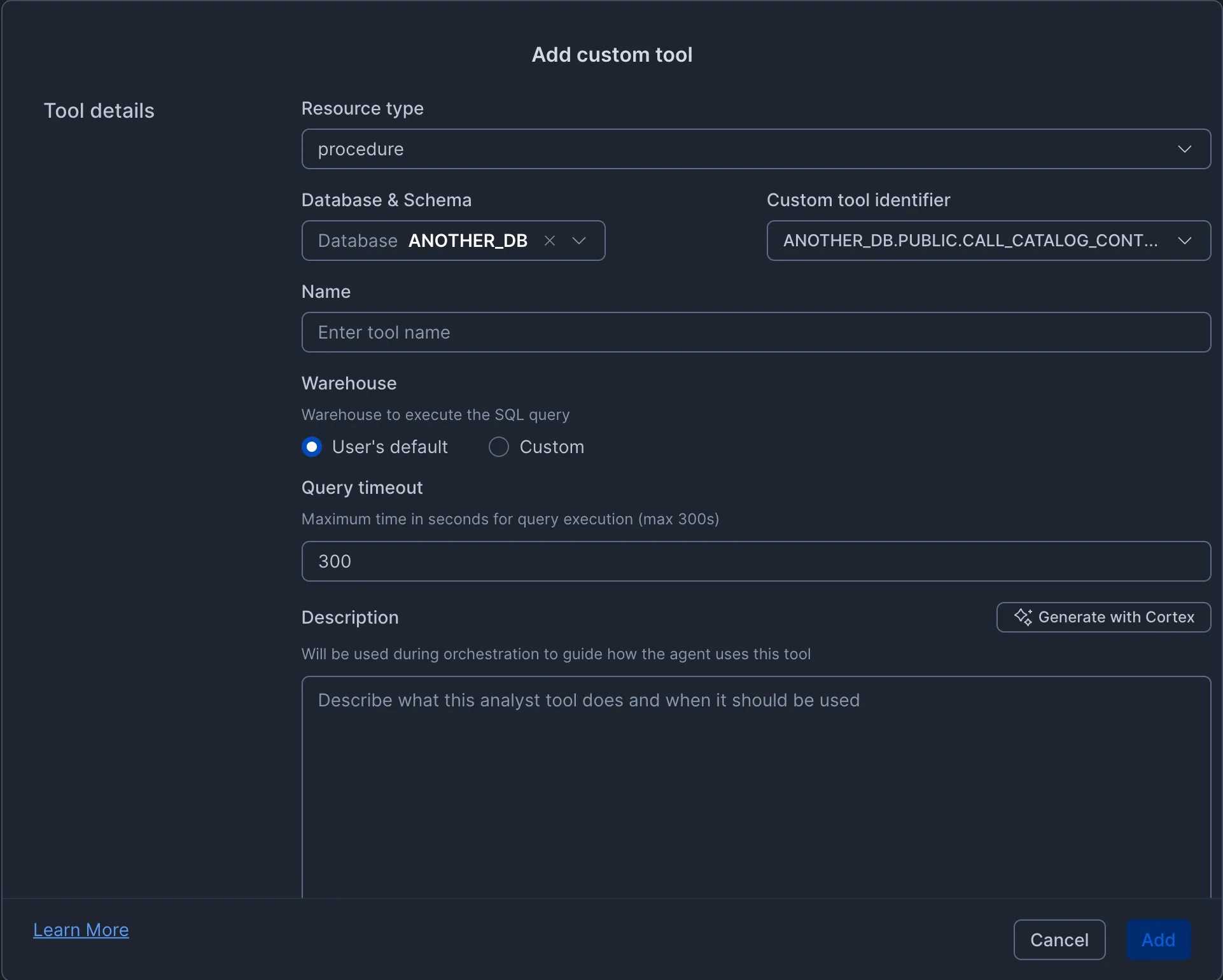
Step 7: Test it out
Section titled “Step 7: Test it out”Once the agent is saved with the custom tool, we can try it out in playground and/or Snowflake intelligence